This is just a quick post about a cool feature of netsh and the successor to Microsoft’s NetMon.
netsh trace
With Windows 7 / Server 2008R2 and newer versions a cool feature has been added to netsh: the possibility to capture network traces without the need to install any third party software.
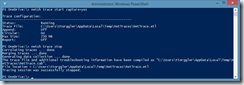
All you need to do is to start an elevated command prompt (run as Admin) and type the following command:
netsh trace start capture=yes
Then do the stuff you want to capture and stop the trace by using:
netsh trace stop
An .etl trace will be generated and the file path is displayed.
Note: if you use the persistent=yes parameter when starting the trace, you can even trace system reboots.
Microsoft Message Analyzer
So NetMon has been around for a while and IT pros around the world still love it, well at least I do ;) Some time ago, Microsoft introduced its successor, a tool by the name of “Message Analyzer”. This tool can to a lot more than just network traces, find some information on the MessageAnalyzer Blog.
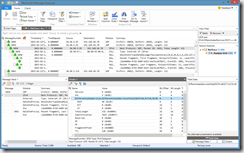
So I just captured a trace using netsh, copied the .etl file to my machine and then opened it in Message Analyzer. As you can see in the screenshot, the layout is quite a bit different from what we’re used from NetMon but the important things are still there.
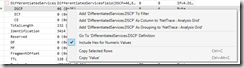
Filtering is quite intuitive, either write an expression into the text box at the right-hand side, or load a filter from the library. Alternatively, just right-click a property of a packet and select “Add to Filter”
Well that’s about all I know about Message Analyzer for now. I was able to verify that packets got tagged with the DSCP values I expected and I did not have to install additional software to capture a trace.
Happy tracing,
Tom