DirectAccess is a feature that has been introduced in Windows Server 2008R2 and Windows 7. It allows secure access to enterprise resources, without requiring a manual VPN connection. A DirectAccess enabled computer establishes a secure connection to the DirectAccess server every time the computer is connected to the internet.
Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8 really simplify the configuration required for DA, making it much easier to deploy a remote access solution.
Requirements
The only requirement is the installation of a Windows Server 2012 member server, providing the “head end” of the connection. No Active Directory, schema, forest, domain-level updates are required.
The DA Server needs two network adapters, one connected to the internal LAN, the other one connected to a DMZ or public network.
If the DA Server is located behind a firewall, https (tcp/443) has do be allowed from the internet to the “public” network adapter.
DirectAccess relies on IPv6 technology, the only hosts that require an IPv6 address are the DirectAccess Server and clients, though. The DA server performs NAT64 and DNS64 in order to enable the DA client to access IPv4 only servers.
Installation
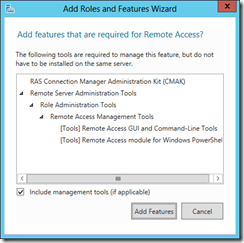
Use ServerManager or PowerShell to install the Remote Access server role on the designated DirectAccess server.
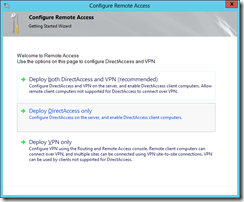
Once installed, use the “Getting started” wizard to configure DirectAccess. The wizard can be started from ServerManager or from within the “Remote Access Management Console”.
Select “Deploy DirectAccess only” in the wizard.
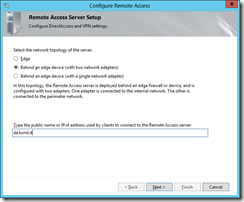
Select the network topology to be used, in this example I am using a server with two network adapters, one connected to a DMZ and one connected to my LAN. Specify the name (or public IP) that clients will be using to connect.
And that’s all there is about it, it’s called “simplified deployment”. The Wizard goes ahead and creates Group Policies for DA Servers and Clients, creates DNS records for Network Location. Pretty cool, eh?
To modify the settings, click the “here” link on the last page of the wizard, for my test environment I go with the defaults.
As the wizard finishes, it shows some information about what it did.
DirectAccess Server
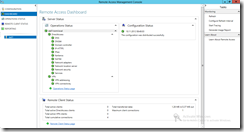
The DirectAccess Configuration can be shown and changed in the Remote Access Management Console.
The Dashboard and Operations Status panels do provide information about the servers status, required services and connected clients.
DirectAccess Clients
The wizard created a Group Policy Object, named “DirectAccess Client Settings” and a WMI Filter, to apply that GPO to Notebooks running Windows 7 or 8 Enterprise editions. So all I had to do was to update the group policies on the notebook (gpupdate).
As long as it was connected to the LAN nothing changed, if I connected the notebook to the internet, the DA (Workplace Connection) was established automatically and I was able to access internal resources as if I was on the LAN.
I think this “simplified deployment” really does make it easier to get started with DirectAccess, to deploy it in an enterprise network, one should be a little more familiar with the technology :)
So this post was meant to be a quick-and-dirty intro, stay tuned for more in-depth information.
so long,
tom